What is the difference between dry type transformer and oilWe have every reason to believe. oil immersed transformer It will become the mainstream of the industry and will gradually affect more and more people. https://www.jslhtf.com/
In power transmission and distribution systems, transformers serve as the core equipment for voltage conversion, directly impacting grid stability, operational costs, and safety.
Oil-immersed and dry-type transformers are the two most widely used types, each with distinct structural designs and performance characteristics. This article provides a professional analysis of their advantages, disadvantages, and application scenarios to guide optimal selection.
Oil-Immersed Transformers: Traditional Power Solutions with Insulating Oil
Oil-immersed transformers use insulating oil (mineral oil or vegetable-based oil) as both the cooling and insulating medium. As the most mature transformer type in the power industry, they dominate high-voltage and large-capacity applications.
Technical Principles and Structural Features
The core design leverages the physical properties of insulating oil for dual functions:
Enhanced Insulation: Insulating oil has a breakdown voltage (25-35kV/mm) far exceeding air (3kV/mm), effectively isolating high-voltage windings from grounded enclosures.
Efficient Heat Dissipation: Through natural convection or forced circulation (with oil pumps), the oil transfers heat from the core and windings to the tank walls or external radiators.
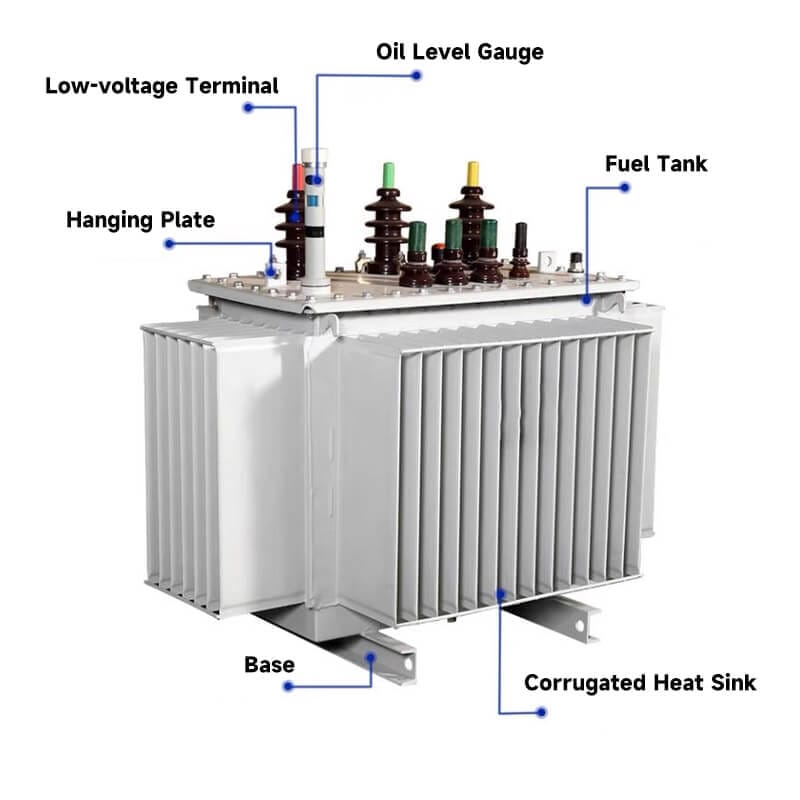
Key components include:
Main Parts: Core, high/low-voltage windings.
Auxiliary Systems: Oil tank, conservator, breather, and explosion vent. The conservator compensates for oil volume changes, the breather adsorbs moisture, and the explosion vent releases pressure during emergencies.
Advantages of Oil-Immersed Transformers
High Capacity and Efficiency
With a thermal conductivity 3-4 times that of air, oil enables large-capacity designs (from hundreds of kVA to tens of MVA). Efficiency reaches 95%-99.5% under full load, ideal for power plants and long-distance transmission.
Superior Insulation Stability and Long Lifespan
The sealed tank environment protects windings from moisture and dust, extending the lifespan to 20-30 years (or over 40 years for premium models), outlasting many dry-type transformers.three phase power transformer
Strong Overload Capacity
It can handle 120%-150% of rated load for short periods (30-60 minutes) and is suitable for fluctuating industrial loads or seasonal demand peaks.
Lower Lifecycle Cost
Manufacturing costs are 20%-40% lower than dry-type transformers for the same capacity. Even with regular maintenance, the total cost of ownership remains competitive.
Limitations of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Safety and Environmental Risks
Traditional mineral oil is flammable (flash point 140-160<C), posing fire hazards if leaked. Spills also contaminate soil and water. While biodegradable vegetable oils mitigate risks, they cost 30% more.
Installation Constraints
Large size and weight (e.g., 1.5-2 tons for a 1000kVA unit, 1.5-2 times heavier than dry-type) require dedicated foundations or outdoor spaces, unsuitable for cramped indoor environments like high-rise basements.
Complex Maintenance
Regular oil testing (dielectric loss, moisture, breakdown voltage) and filtration/replacement every 1-2 years increase maintenance labor and costs.
Dry-Type Transformers: Modern Oil-Free Power Solutions
Dry-type transformers use air or inert gas for cooling and solid insulation
materials (e.g., epoxy resin, Nomex paper), making them ideal for indoor and environmentally sensitive applications.
Technical Principles and Structural Features
Heat dissipation relies on natural air convection or forced air cooling. The insulation system consists entirely of solid materials:
Winding Insulation: Cast resin transformers encase windings in epoxy for moisture and dust resistance; impregnated transformers coat windings with insulating varnish.
Core Design: Similar to oil-immersed types but uses lower-loss
silicon steel (e.g., 30Q130) to reduce heat generation.
Common types include epoxy cast resin (most prevalent, ~80% market share), open-frame, and encapsulated designs, with cast resin dominating in harsh environments.
Advantages of Dry-Type Transformers
Superior Safety and Environmental Compatibility
No flammable oil eliminates fire risks, making them suitable for high-rise buildings, hospitals, data centers, and subway stations. They also meet strict environmental regulations with zero oil leakage.
Compact Size and Flexible Installation
30%-40% smaller and lighter than oil-immersed units of the same capacity, enabling installation in indoor switchgear, on floors, or brackets, saving valuable space in urban areas.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Eliminate oil testing and replacement. Routine maintenance involves annual dust cleaning and connection checks, reducing labor costs, especially in high-wage regions.
Excellent Environmental Adaptability
Epoxy-encased windings withstand humidity up to 90% (non-condensing) and dusty environments, making them ideal for basements, coastal areas, and industries like textiles or food processing.
Limitations of Dry-Type Transformers
Limited Cooling Efficiency and Capacity
Air¨s low thermal conductivity (0.026W/(m,K)) restricts capacity to +2500kVA (natural cooling) or +5000kVA (forced air), insufficient for large industrial plants or high-voltage substations.
Environmental Sensitivity
Solid insulation ages faster under high temperatures (>100<C) or humidity (condensation). Dust accumulation on windings can cause partial discharges, shortening lifespan.
Weaker Overload Capacity
Can only handle 110%-120% of rated load for +30 minutes, unsuitable for applications with frequent load fluctuations.
Higher Initial Cost
Premium materials and manufacturing processes increase costs by 30%-50% compared to oil-immersed transformers, particularly for small-capacity units (<500kVA).